Xiaomi this week introduced its first in-house flagship chipset, the Xring O1, powering both the Xiaomi 15S Pro smartphone and the Xiaomi Pad 7 Ultra tablet. Despite initial skepticism—given its use of ARM’s standard Cortex-X925 CPU cores and Immortalis-G925 GPU—the Xring O1 represents a deeply customized mobile processor that delivers leading CPU performance and energy efficiency.
Manufactured on TSMC’s N3E node (the same 3 nm process behind MediaTek’s Dimensity 9400), the Xring O1 departs from reference designs by incorporating two Cortex-X925 prime cores instead of just one. Xiaomi also chose a bespoke mix of six Cortex-A725 cores—split into four high-frequency cores clocked at 3.4 GHz and two efficiency-tuned cores at 1.9 GHz—in lieu of the more common Cortex-X4 cluster. Two extra Cortex-A520 cores provide a low-power fallback, although the robust A725 cores may render them redundant.
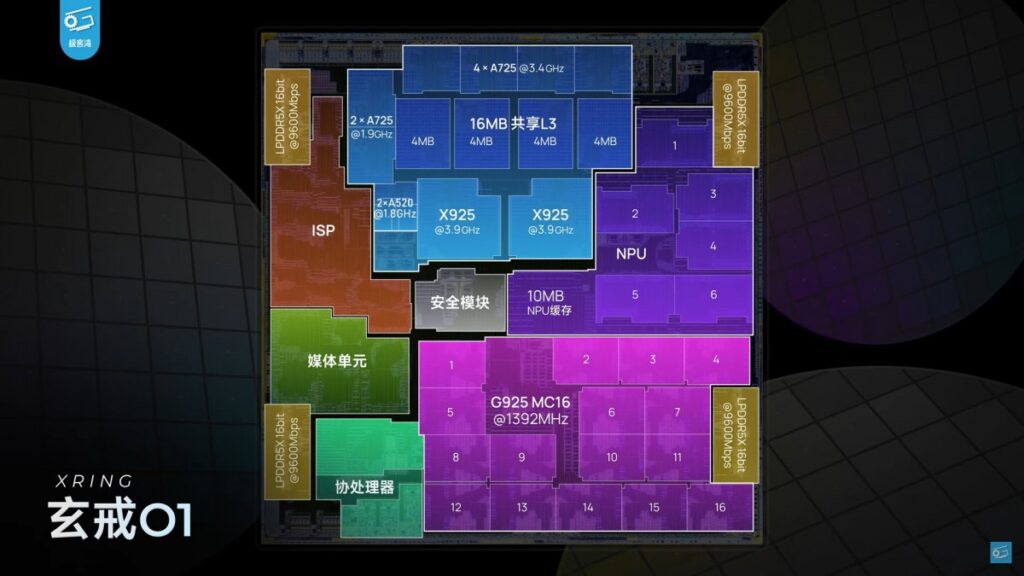
Xiaomi’s cache architecture further differentiates the Xring O1. Rather than a traditional System Level Cache (SLC), Xiaomi allocated 16 MB of L3 cache shared across all ten cores, 2 MB of L2 per Cortex-X925 core, 1 MB of L2 per Cortex-A725 core, 4 MB for the GPU, and a staggering 10 MB for the custom six-core NPU. This cache-heavy approach minimizes energy-hungry DRAM access and boosts real-world performance.
In benchmarks, the Xring O1 outpaces the Dimensity 9400 in both single-core and multi-core CPU tests and approaches the efficiency of Qualcomm’s Snapdragon 8 Elite, despite lacking an integrated 5G modem. Instead, Xiaomi relies on an external MediaTek T800 modem—an arrangement that contributes to the chip’s compact 109 mm² die size, comparable to Apple’s A18 Pro.
The custom NPU and a fourth-generation in-house ISP further underscore Xiaomi’s vertical integration ambitions. While the 16-core Immortalis-G925 GPU delivers strong graphics power, it consumes more energy at peak loads—an efficiency trade-off that Xiaomi will likely refine in future revisions.
By launching the Xring O1, Xiaomi joins the ranks of companies developing proprietary mobile silicon, following its initial foray with the Xring T1 4G modem chipset for the Xiaomi Watch S4. Achieving a fully integrated 5G modem on-chip remains a future milestone, one Apple reached after years of development with its iPhone 16e.
Xiaomi’s bold move into custom chipset design with the Xring O1 demonstrates its commitment to optimizing both performance and power efficiency, setting the stage for even tighter hardware-software integration across its device ecosystem.